The Art of Hospitality: Definition, Global Importance, Strategies, and Etiquette
The art of hospitality is more than just welcoming guests; it is an age-old tradition rooted in kindness, generosity, and service. Across cultures and continents, hospitality plays a vital role in fostering connections, loyalty, and trust. Whether in a luxury hotel, a fine dining restaurant, or a family home, the art of hospitality defines how people feel valued and respected.
This article delves into:
The definition and importance of hospitality
Its global significance across cultures
Effective strategies for delivering outstanding hospitality
Etiquette and protocols that enhance guest experience
1. What is the Art of Hospitality? Definition and Concept
A. Definition of Hospitality
The art of hospitality refers to the practice of providing care, comfort, and entertainment to guests or visitors. It goes beyond mere service; it is about creating memorable experiences through warmth, professionalism, and attention to detail.
In the words of Maya Angelou:
“People will forget what you said, forget what you did, but people will never forget how you made them feel.”
B. Core Principles of Hospitality:
- Welcome: Offering a warm and genuine greeting.
- Comfort: Ensuring guests feel at ease and attended to.
- Generosity: Going beyond expectations to delight guests.
- Personalization: Tailoring experiences to individual preferences.
- Courtesy: Showing politeness, respect, and professionalism.
C. Areas Where Hospitality Shines:
- Hotels and Resorts: Front desk services, room service, and concierge experiences.
- Restaurants and Cafés: Customer service, ambiance, and culinary excellence.
- Airlines and Cruises: In-flight services, lounges, and personalized care.
- Retail and Corporate Sectors: Client relationship management and personalized service.
- Private Homes: Guest preparation, hosting meals, and providing comfort.
2. The Globality of Hospitality: Cultural Perspectives Around the World
A. Universal Tradition, Diverse Practices
While the core values of hospitality are universal, each culture has its unique customs and rituals that shape how they welcome and treat guests. Let’s explore the art of hospitality across continents:
1. Middle Eastern Hospitality: Generosity and Honor
- Known for its extravagance and warmth, Middle Eastern hospitality often includes lavish meals, coffee rituals (e.g., Arabic coffee), and personalized attention.
- It is common to insist on guests staying longer and refusing compensation, as generosity is considered a moral virtue.
2. Japanese Hospitality (Omotenashi): Respect and Precision
- Rooted in Zen and tea ceremony traditions, Omotenashi is about anticipating guests’ needs and serving them with sincerity and grace.
- Service is performed without expectation of reward, and attention to detail is paramount.
3. Moroccan Hospitality: Warmth and Tea Rituals
- Moroccan hospitality is marked by offering mint tea, a symbol of friendship and respect.
- Guests are treated with great honor, and meals are shared from a communal plate, fostering a sense of togetherness.
4. French and European Hospitality: Elegance and Refinement
- Focuses on politeness, fine dining, and quality service.
- Etiquette is crucial, from proper table settings to formal greetings (e.g., “Bonjour” and cheek kisses).
5. American Hospitality: Informality and Friendliness
- Known for friendly service, openness, and inclusiveness.
- Phrases like “How can I help you?” and “Enjoy your meal!” are part of the hospitality culture.
6. African Hospitality: Community and Generosity
- African hospitality emphasizes community values and sharing.
- It is customary to offer food and shelter without expectation, as guests are seen as “blessings from God.”
7. Italian Hospitality: Warmth and Culinary Delight
- Centered around family gatherings and shared meals.
- Guests are treated with warmth, and homemade food is a common gesture of love and care.
3. Strategies for Providing Outstanding Hospitality
A. Mastering the Guest Journey
From the first interaction to the farewell, each moment shapes the guest’s perception. Focus on:
- First Impressions: Greet with a smile and enthusiasm.
- Smooth Onboarding: Ensure easy check-ins, reservations, and introductions.
- Attention to Needs: Proactively address guest requests.
- Farewell and Follow-Up: End experiences with gratitude and maintain relationships.
B. Personalization and Anticipation of Needs
- Use Guest Profiles: Collect preferences (e.g., favorite drinks or room settings).
- Offer Surprises: Small gestures like a welcome note or a complimentary upgrade.
- Remember Special Occasions: Celebrate birthdays or anniversaries.
C. Training and Empowering Staff
- Soft Skills Development: Train staff in communication, empathy, and conflict resolution.
- Role-Playing Scenarios: Practice handling difficult situations (e.g., guest complaints).
- Empower Decision-Making: Allow staff to resolve minor issues independently.
D. Creating an Inviting Atmosphere
- Ambiance Matters: Pay attention to lighting, music, cleanliness, and décor.
- Scents and Sounds: Use sensory experiences (e.g., soft music or fresh flowers).
- Comfort First: Provide comfortable seating, climate control, and soft furnishings.
E. Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Service
- Contactless Services: Mobile check-ins and digital menus.
- AI Chatbots: Provide instant customer support.
- CRM Systems: Maintain detailed customer profiles for personalized service.
4. The Etiquette of Hospitality: Rules for Memorable Experiences
A. Welcoming Etiquette
- Stand, smile, and make eye contact when greeting guests.
- Use polite language and titles (“Mr./Mrs.”) unless invited to be informal.
- Offer refreshments immediately if appropriate.
B. Communication Etiquette
- Listen actively and respond thoughtfully.
- Avoid negative phrases; use positive framing (e.g., “Let me see what I can do” instead of “No”).
- Speak clearly and be culturally sensitive to gestures and expressions.
C. Dining and Service Etiquette
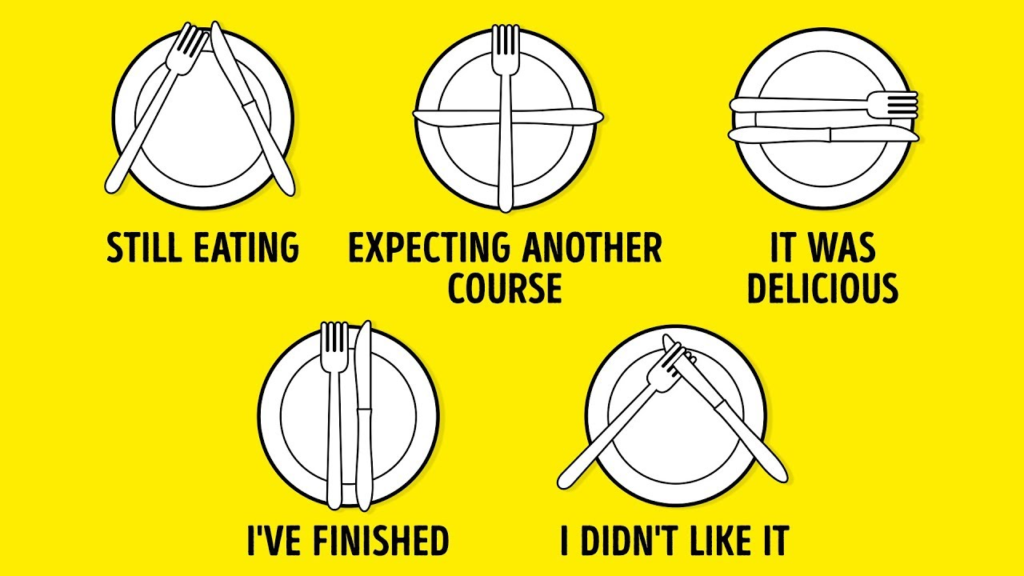
- Serve guests from their left and remove dishes from the right (Western style).
- Be familiar with cutlery placement and wine service protocols.
- Always serve the eldest or most distinguished guest first.
D. Conflict Resolution Etiquette
- Apologize sincerely if a guest is dissatisfied.
- Acknowledge their feelings and offer immediate solutions.
- Follow up with a compensatory gesture (e.g., discounts, complimentary items).
E. Farewell Etiquette
- Always thank the guest for their visit.
- Offer assistance with departures (e.g., luggage, transportation).
- Follow up with a thank-you email or feedback request.
5. Measuring Success in Hospitality: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
A. Guest Satisfaction Scores (GSS):
Collect feedback through surveys or online reviews (e.g., TripAdvisor, Google).
B. Net Promoter Score (NPS):
Measure how likely guests are to recommend your service.
C. Repeat Guest Rate:
Track how many customers return, indicating loyalty.
D. Average Revenue per Guest (ARPG):
Evaluate revenue generated from additional services (e.g., room upgrades, dining).
E. Employee Satisfaction:
Happy employees often result in happy guests, so monitor staff morale.
6. The Future of Hospitality: Trends and Innovations
A. Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Hospitality:
- Green initiatives (e.g., plastic-free policies, solar energy).
- Local sourcing of ingredients and products.
B. Smart Technology:
- Virtual reality (VR) tours.
- AI-powered concierge services.
C. Experiential Tourism:
- Offering immersive experiences (e.g., cooking classes or cultural tours).
- Promoting wellness retreats and mindful travel experiences.
D. Emotional Intelligence in Service:
- Training staff to read guest emotions and respond empathetically.
- Using human-centered design for hospitality spaces.
The Art of Hospitality as a Global Language
The art of hospitality transcends cultures and industries, creating lasting memories and fostering relationships. It combines skill, etiquette, empathy, and strategy to make every guest feel special. Whether through a smile, a personalized note, or seamless service, true hospitality leaves a lasting impression.
In an increasingly globalized world, mastering the art of hospitality requires understanding cultural nuances, embracing innovation, and consistently exceeding expectations.
Rules of Etiquette and Protocols: A Guide to Professional and Social Excellenc
Etiquette and protocols are essential for creating a respectful, courteous, and professional environment. While etiquette governs personal behavior and social norms, protocols are formal rules that regulate official events, business conduct, and diplomacy. Together, they ensure politeness, order, and clarity in various interactions.
This article covers:
✅ The definitions of etiquette and protocols
✅ Key rules of etiquette for different settings
✅ Essential protocols for formal events and diplomacy
✅ The differences between etiquette and protocol
1. Understanding Etiquette and Protocols
A. What is Etiquette?
Etiquette refers to customary rules of behavior that are considered polite and appropriate in social, professional, and cultural settings. It is based on respect, consideration, and empathy.
Examples:
- Saying “Thank you” and “Please” in conversations.
- Shaking hands upon meeting someone.
- Dressing appropriately for occasions.
B. What are Protocols?
Protocols are formalized rules and procedures that govern official conduct in ceremonies, diplomacy, and business settings. They are more structured than etiquette and often carry legal or institutional significance.
Examples:
- Seating arrangements at a state banquet.
- The order of flags during an international conference.
- The proper way to address dignitaries.
C. Difference Between Etiquette and Protocol
| Aspect | Etiquette | Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Polite behavior based on social norms | Formal rules for official or ceremonial conduct |
| Scope | Informal and adaptable | Formal and structured |
| Context | Social, professional, and cultural | Government, diplomacy, and corporate settings |
| Flexibility | Flexible, can vary by culture | Strict and based on precedence or hierarchy |
| Example | Holding the door open for someone | Seating a head of state according to rank |

2. Rules of Etiquette in Different Settings
💼 A. Business Etiquette
- Greetings: Shake hands firmly and maintain eye contact.
- Punctuality: Always be on time for meetings.
- Dress Code: Dress appropriately (business formal or business casual).
- Communication: Use polite and professional language in emails and calls.
- Respect Hierarchies: Address senior colleagues by their titles unless told otherwise.
- Active Listening: Do not interrupt during conversations or meetings.
🍽️ B. Dining Etiquette
- Table Manners: Keep elbows off the table and chew with your mouth closed.
- Use of Cutlery: Start with the outermost utensils and work inward.
- Napkin Etiquette: Place your napkin on your lap when seated.
- Serving: Pass food to the right and always offer to others first.
- Toasting: Maintain eye contact when clinking glasses.
- Payment: In professional settings, the host pays the bill.
🗺️ C. Cross-Cultural Etiquette
- Greetings: Bowing in Japan, cheek kissing in France, or handshakes in the U.S.
- Gift-Giving: Bring gifts when visiting someone’s home (common in many Asian and Middle Eastern cultures).
- Dress Codes: Respect local customs (e.g., covering shoulders in conservative regions).
- Body Language: Avoid gestures that may be offensive (e.g., pointing with one finger in some countries).
- Communication Styles: Be aware of cultural differences in tone, volume, and formality.
📱 D. Digital Etiquette (Netiquette)
- Email Etiquette: Use clear subject lines, proper greetings, and concise language.
- Virtual Meetings: Dress appropriately, mute your microphone when not speaking, and maintain eye contact via the camera.
- Social Media: Be respectful and avoid sharing inappropriate content.
- Response Time: Reply to emails or messages promptly.
3. Rules of Protocol for Formal Events and Diplomacy
A. Protocol for Ceremonies and Official Events
- Order of Precedence: Follow the hierarchy when introducing guests or arranging seating.
- Flag Etiquette: Display national flags correctly, with the host country’s flag on the left from the viewer’s perspective.
- Seating Arrangements: Use the proper seating order (e.g., head of state in the center, dignitaries on the right).
- National Anthems: Stand during the playing of national anthems and observe silence.
B. Diplomatic Protocol
- Titles and Address: Use proper titles (“Your Excellency,” “Madam Ambassador”).
- Presentation of Credentials: Formal ceremonies for ambassadors presenting their credentials to the head of state.
- Gift Exchanges: Choose culturally appropriate and symbolic gifts.
- Language: Use formal and respectful language in diplomatic notes and speeches.
- Dress Code: Adhere to formal or traditional attire as per the event.
C. Corporate Protocol
- Introductions: Present senior executives or distinguished guests first.
- Meeting Procedures: Begin with an agenda and follow proper meeting formats.
- Conference Seating: Arrange seating based on rank and title.
- Business Cards: Exchange business cards respectfully, accepting with both hands in some cultures.
4. Etiquette and Protocol in Hospitality
In the hospitality industry, etiquette and protocol ensure exceptional guest experiences and maintain the reputation of establishments.
A. Hotel Hospitality Protocols
- Welcoming Guests: Greet guests with a smile and use their names whenever possible.
- Check-in/Check-out: Be efficient and polite, explaining all services clearly.
- Handling Complaints: Listen carefully, apologize sincerely, and resolve issues promptly.
- Room Service: Knock three times and announce yourself before entering.
🍽️ B. Restaurant Hospitality Etiquette
- Server Etiquette: Approach guests with a smile, introduce yourself, and be attentive without being intrusive.
- Order Protocol: Take orders starting from the eldest or the most distinguished guest.
- Serving Drinks: Serve from the right and remove dishes from the left.
- Bill Settlement: Present the check discreetly and thank guests upon their departure.
5. Importance of Etiquette and Protocol in Professional and Social Life
✅ A. Builds Strong Relationships:
- Etiquette fosters respect and trust, making interactions smoother.
- Protocol clarifies expectations in formal settings, reducing misunderstandings.
✅ B. Promotes Inclusivity and Respect:
- Understanding cross-cultural etiquette ensures inclusivity and prevents offense.
- Proper protocol honors rank and tradition, making everyone feel valued.
✅ C. Enhances Professionalism:
- In business, etiquette and protocol create a positive impression, building credibility and rapport.
✅ D. Supports Diplomacy:
- In international relations, protocol prevents conflicts and promotes smooth interactions.
🌟 6. Mastering Etiquette and Protocol: Tips for Success
- ✅ Observe: Learn from experienced individuals and adapt to different cultural contexts.
- ✅ Ask Questions: When unsure, politely ask about local customs or formalities.
- ✅ Practice Active Listening: Show empathy and respect during conversations.
- ✅ Stay Polite Under Pressure: Remain composed, especially during conflicts.
- ✅ Dress Appropriately: Always dress for the occasion.
- ✅ Be Punctual: Respect others’ time by arriving on time.
- ✅ Maintain Confidentiality: Respect private information, especially in business settings.
Etiquette and protocols are more than rules; they are expressions of respect, empathy, and professionalism. Mastering them opens doors to stronger relationships, smoother interactions, and better opportunities in both personal and professional settings.